New Research
Swimming in Schools May Help Fish Save Energy in Turbulent Waters
A new study suggests schooling fish use up to 79 percent less energy in rough conditions than fish that swim alone
When Vultures Nearly Disappeared in India, Half a Million People Died, Too, Study Finds
By being nature's clean-up crew, the often maligned birds help prevent the spread of diseases, according to a new study
Hidden Underground Magma Pools Fueled Iceland's Volcanic Eruptions, Study Suggests
A subterranean plumbing system of magma beneath the island’s Reykjanes Peninsula may have helped set off the recent series of eruptions that could last for centuries
Static Electricity May Help Butterflies and Moths Pick Up Pollen
A new study measured the insects' electrostatic charges and used computer simulations to show that the charges were strong enough to lift pollen
Why Are Giant, Ancient Tropical Trees Dying?
Scientists from an international project are racing to figure out what kills these anchors of their ecosystems—before it's too late to save them
Early Humans Migrated Out of Africa Several Times, DNA Study Suggests
Homo sapiens interbred with Neanderthals as early as 250,000 years ago and may have ultimately bred them out of existence, according to new research
The Largest T. Rex Could Have Been 70 Percent Heavier Than Fossils Suggest
Two scientists used modeling to predict how big the giant carnivores could have really grown, making a point that fossils likely don't represent the largest or smallest individuals of a species
Ancient Mesoamerican 'Pyramid of the Moon' May Align With Summer and Winter Solstices
New research suggests the monument in Teotihuacán, along with the larger Pyramid of the Sun, were designed based on astronomical movements
Komodo Dragons Have Iron-Coated Teeth, Study Finds
New research provides the first evidence of the adaptation in a carnivorous reptile, and it might hold clues to understanding the teeth of dinosaurs
Alzheimer's Blood Test Outperforms Standard Diagnostics in New Study
The blood test accurately diagnosed Alzheimer's around 90 percent of the time, compared to 73 percent for specialists and 61 percent for primary care physicians
Two Rare Jurassic Skulls Could Help Unlock the Secrets of Mammals' Evolutionary Success
Fossils reveal a prehistoric, mouse-like creature matured slower and lived longer than similar mammals of today
Taco-Shaped Creature Had a 'Major Edge' in Evolution—and 30 Pairs of Spiny Legs
This shrimp-like arthropod was among the first to have a mandible, and it used a complex feeding mechanism during the Cambrian explosion, according to a new study
Scientists Discover 'Dark Oxygen' on the Ocean Floor Generated—Surprisingly—by Lumps of Metal
Researchers found that electric currents from polymetallic nodules are behind this alchemy—the same minerals that deep-sea miners are targeting
The Smell of Human Stress Leads Dogs to Make More Pessimistic Decisions, Study Suggests
Canines that smelled the sweat of anxious people were less likely to approach a bowl that might have contained food, indicating humans' emotions can affect dogs' behavior
The 'World's Loneliest Plant' Could Soon Find a Mate With a Little Help From A.I.
The only known wild Wood's cycad was discovered in 1895, and it has since been cloned into many male trees. Now, researchers are scouring a forest in South Africa for an elusive female specimen
Thirteen Sharks Test Positive for Cocaine Off the Coast of Brazil
All of the wild Brazilian sharpnose sharks tested in a new study had the drug in their bodies, but many questions remain about cocaine's effects on aquatic creatures—and the humans who eat them
Chimpanzees Take Turns in Fast-Paced Conversations, Just Like Humans Do
A new study finds the average chimpanzee response time in gestured conversations is 120 milliseconds, which isn’t that far from the human average of 200 milliseconds
Geologists Uncover Remnants of Earth’s Mantle That Have Lasted Over 2.5 Billion Years
New research suggests that a discrepancy in rocks shows they endured extreme heat, and reveals more about an ancient part of our planet’s history
Common Blood Thinners Could Combat Snakebites, Preventing Tissue Damage and Amputations, Study Finds
An estimated 400,000 people per year are permanently disabled because of snake venom, which can cause lesions and necrosis at the bite site
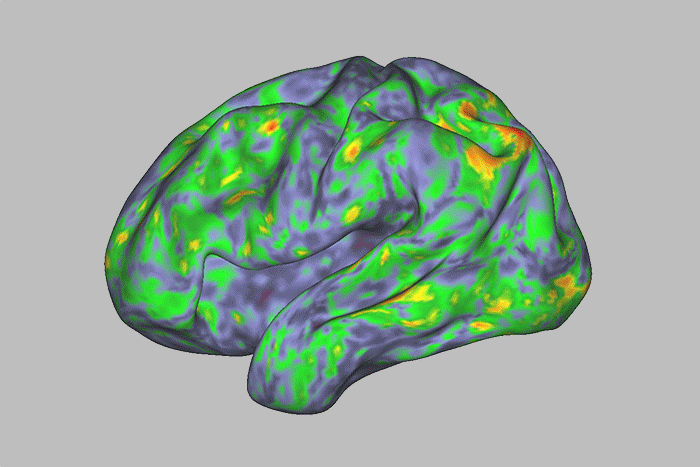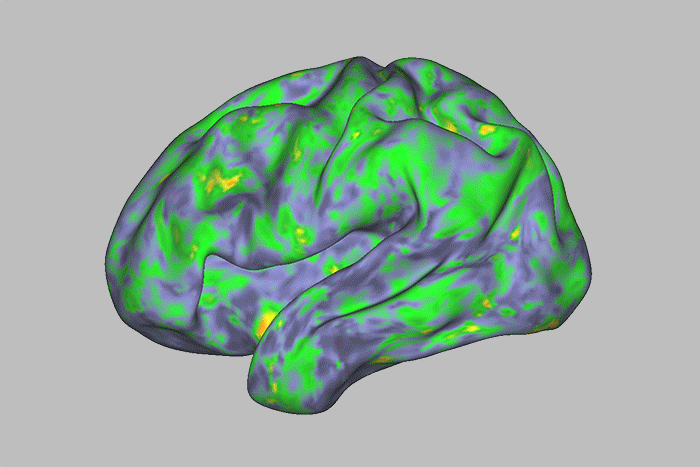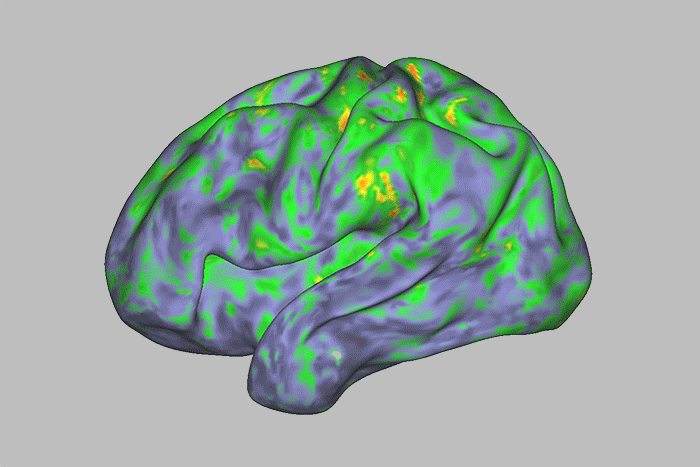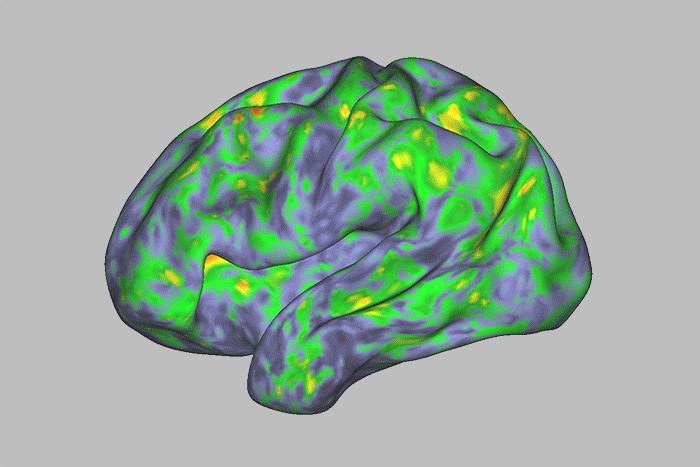
See How the Brain Responds to Psychedelic 'Magic Mushrooms'
A new study mapped large, temporary changes in brain areas related to introspection and one's sense of self, after participants took a dose of the drug psilocybin
Page 3 of 250
:focal(400x267:401x268)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/8a/c2/8ac2313e-8451-4a92-9118-cbec3d3ece70/school_jacks_klein.jpeg)
:focal(3000x2000:3001x2001)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/f1/9d/f19dbd8f-ad20-496f-9665-07852d3bf051/gettyimages-1241170086.jpg)
:focal(1512x1138:1513x1139)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/21/fe/21fe87b7-82ae-415f-b634-0d46f0005c6c/gettyimages-2155900823.jpg)
:focal(3024x2016:3025x2017)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/df/cb/dfcbaa9d-9fc7-4124-a123-8173a5dce198/gettyimages-1243935899.jpg)
:focal(2464x1643:2465x1644)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/79/2b/792bd175-4567-4c8f-b685-777ca304e1ef/gettyimages-500241484.jpg)
:focal(1750x1175:1751x1176)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/97/36/973642de-8855-4633-93eb-3facdabad0ea/gettyimages-853018002.jpg)
:focal(3352x745:3353x746)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e2/26/e2264891-48be-4dee-b8b6-6cee0f278c86/scotty_tyrannosaurus.jpg)
:focal(1217x695:1218x696)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/94/fe/94fe3973-2740-4409-adad-73d06c3c9a75/piramide_de_la_luna_072006.jpg)
:focal(2429x1619:2430x1620)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/4f/e6/4fe6bcc6-7ff9-4947-9f62-464712cff3bb/gettyimages-2123610440.jpg)
:focal(1061x707:1062x708)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/24/2f/242f7b45-9432-4e4d-9deb-1beb7c4845a9/gettyimages-1443155227.jpg)
:focal(1500x1014:1501x1015)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/6b/ce/6bce8196-1278-45c6-972f-db89449b29df/krusatodon_kirtlingtonesis_artist_impression_credit_maija_karala.jpg)
:focal(350x273:351x274)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/cb/d2/cbd26d57-53f0-46b1-80ec-6ddd33adfd75/low-res_odaraia_life_reconstruction_by_danielle_dufault.jpg)
:focal(1969x1322:1970x1323)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/c5/ca/c5ca9228-e647-4dde-8989-dffcfc211b88/gettyimages-1234090606.jpg)
:focal(1060x712:1061x713)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/d4/37/d43735f1-067f-4070-b186-7cc2999185b0/gettyimages-1463449494.jpg)
:focal(700x500:701x501)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/d2/49/d2492998-8601-4205-b203-48a7835f5802/laura.jpg)
:focal(800x602:801x603)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/d5/14/d514ed7e-999b-43ca-bc53-bf78237f9f04/image2_3.jpeg)
:focal(3000x2000:3001x2001)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/15/79/15798be8-6e39-4b96-a2a6-ef5bcfb98f79/aso_3241.jpg)
:focal(1004x1243:1005x1244)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/e5/a4/e5a47313-945c-40c7-82a9-f72cb9e71a5b/a2_-_elizabeth_cottrell_-_hly102-40-56__5.jpg)
:focal(2589x1726:2590x1727)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/78/c1/78c1bfdc-32e7-46fa-9065-5292db955971/gettyimages-200352535-001.jpg)